
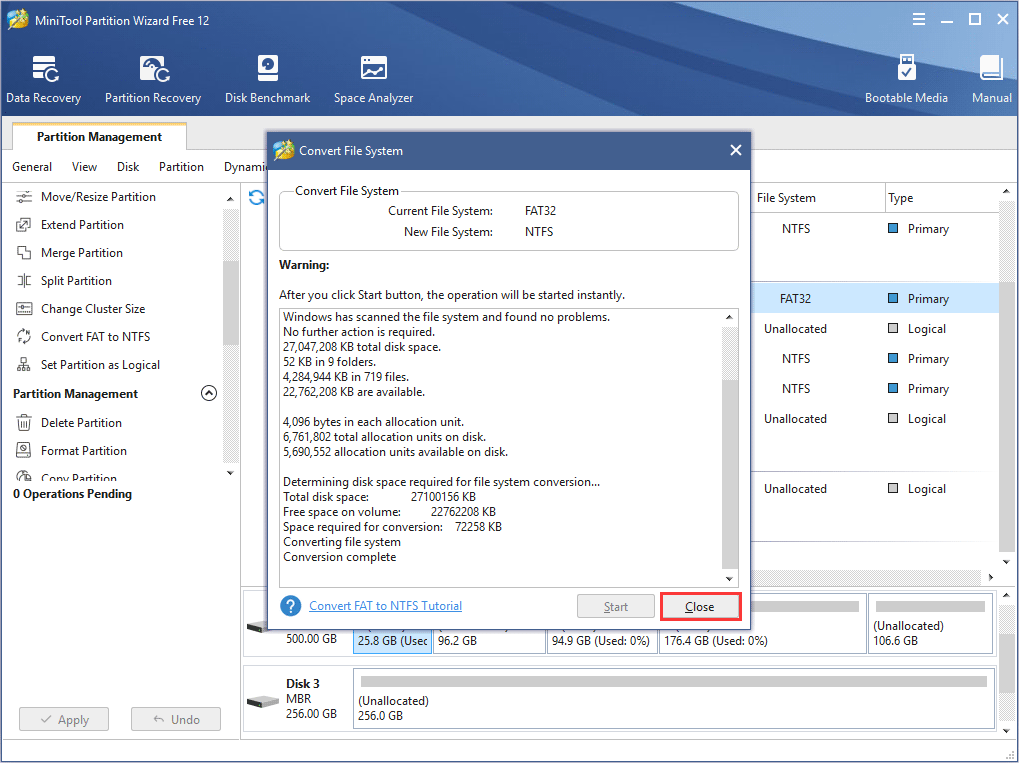
Fat32 or ntfs archive#
In addition, FAT supports only read-only, hidden, system, and archive file attributes. There is no organization to the FAT directory structure, and files are given the first open location on the drive. It is time consuming because the disk read heads must be repositioned to the drive's logical track zero each time the FAT table is updated. If the FAT table is not regularly updated, it can lead to data loss. Updating the FAT table is very important as well as time consuming. This entry in the FAT table either indicates that this is the last cluster of the file, or points to the next cluster. When a file is created, an entry is created in the directory and the first cluster number containing data is established. In addition, the FAT tables and the root directory must be stored in a fixed location so that the system's boot files can be correctly located.Ī disk formatted with FAT is allocated in clusters, whose size is determined by the size of the volume. To protect the volume, two copies of the FAT are kept in case one becomes damaged. The FAT file system is characterized by the file allocation table (FAT), which is really a table that resides at the very "top" of the volume.
Fat32 or ntfs windows#
FAT overviewįAT is by far the most simplistic of the file systems supported by Windows NT. Also, support for the FAT32 file system became available in Windows 98/Windows 95 OSR2 and Windows 2000. Windows NT 4.0 does not support and cannot access HPFS partitions.

HPFS is only supported under Windows NT versions 3.1, 3.5, and 3.51.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
